Article By Dr B. A Onsongo, Wellness Doctor


- How many people do you know with distended bellies who believe they are in good shape? Globally, more than 1.9 billion adults (39% of adults) aged 18 years and older were overweight. Of these over 650 million adults (13% of the world’s adult population) were obese.
- Obesity makes you more likely to have high blood pressure and unhealthy cholesterol levels, which are risk factors for heart disease and strokes. Obesity can also affect the way the body uses insulin to control blood sugar levels.
In this issue, we shall focus on understanding obesity: the causes, health risks and lifestyle management strategies including sample juices for weight reduction.
Obesity is a complex and multifaceted health condition that extends far beyond the simple notion of carrying extra weight. In fact, it’s a chronic disease that affects more than 650 million adults worldwide and is associated with numerous serious health complications. Addressing obesity is not just about fitting into a smaller clothing size; it’s about improving overall health and quality of life. Obesity in the United States currently affects approx.100.1 million (41.9%) adults. In the USA, 2030 projection- 85% will be overweight or obese
Statistics show that obesity rates have nearly tripled since 1975, making it one of the most pressing public health challenges of our time. It’s a condition that affects people of all ages, genders, and backgrounds, with significant impacts on both physical and mental health. Beyond the aesthetic concerns, obesity is linked to a range of chronic diseases, including heart disease, diabetes, and certain types of cancer.
Obesity is a condition where a person has an excessive amount of body fat. It’s often measured using the Body Mass Index (BMI), which is a calculation based on height and weight. : Weight divided by height squared (weight in kilograms and height in metres)
Here are the BMI categories:
- Underweight: BMI less than 18.5
- Normal weight: BMI 18.5-24.9
- Overweight: BMI 25-29.9
- Moderate (Class 1) Obesity: BMI 30-34.9
- Severe (Class 2) Obesity: BMI 35 – 39.9
- Morbid (Class 3) Obesity: BMI > 40
A BMI of 30 or higher is classified as obese. However, it’s important to understand that BMI does not measure body fat directly. For instance, a highly muscular person may have a high BMI but low body fat. Additionally, the distribution of fat in the body matters; visceral fat (fat around the organs) is more harmful than subcutaneous fat (fat under the skin).
Therefore, while BMI is a useful screening tool, it should be considered alongside other factors such as waist circumference, overall body composition, and underlying health conditions to provide a more comprehensive understanding of an individual’s health status.



MAJOR CAUSES OF OBESITY
Although there are genetic, behavioral, metabolic and hormonal influences on body weight, obesity occurs when you take in more calories than you burn through typical daily activities and exercise. Your body stores these excess calories as fat.
- Poor Diet -Consuming high-calorie foods, sugary drinks, and large portion sizes can lead to weight gain. Diets high in fat and sugar, and low in fruits, vegetables, and whole grains contribute to obesity.
- Lack of Physical Activity – Not getting enough exercise is a major factor. Sedentary activities, such as watching TV and using computers, contribute to weight gain.
- Genetics – Family history can play a role in obesity. Certain genetic factors can affect how your body stores fat and how efficiently it converts food into energy.
- Medical Conditions – Some health conditions, such as hypothyroidism (underactive thyroid) and polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS), Cushing syndrome, Prader-Willi syndrome can lead to weight gain or make it harder to lose weight.
- Other Lifestyle Factors – Stress, lack of sleep, and certain medications can contribute to weight gain. Stress and emotional factors can lead to overeating or unhealthy eating habits.
COMPLICATIONS/RISKS ASSOCIATED WITH OBESITY
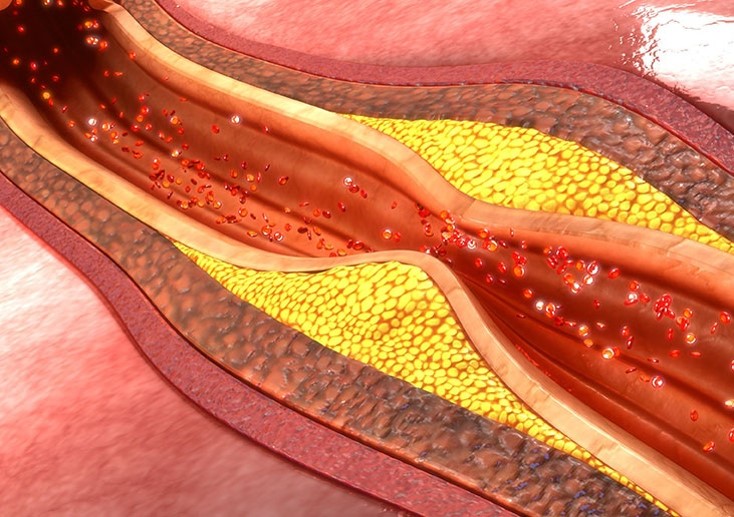
Obesity increases risk for metabolic syndrome which is a cluster of conditions that occur together i.e. increased blood pressure, high blood sugar/insulin resistance & abnormal cholesterol in blood. The above conditions increases your risk of several serious health conditions:
- Heart Disease & Stroke: Obesity makes you more likely to have high blood pressure and unhealthy cholesterol levels, which are risk factors for heart disease and strokes.
- Type 2 Diabetes: Obesity is a major risk factor for developing type 2 diabetes. Excess body fat can lead to insulin resistance, where the body doesn’t use insulin effectively.
- Joint Problems: Excess weight puts additional stress on joints, leading to conditions like osteoarthritis. This can cause pain and mobility issues.
- Sleep Apnea: Obesity increases the risk of sleep apnea, a condition where breathing stops and starts during sleep. This can lead to poor sleep quality and other health issues.
- Certain Cancers: Obesity is linked to an increased risk of several types of cancer, including breast, colon, and endometrial cancer.
- Fatty liver disease. Obesity increases the risk of fatty liver disease, a condition that happens due to excessive fat deposit in the liver. In some cases, this can lead to serious liver damage, known as liver cirrhosis.

HOW TO MANAGE OBESITY
Losing weight when obese or overweight requires more than just limiting the intake of calories. Exercising, facilitating liver function, water, replacing meals with healthy drinks are all necessary. Here are some key strategies:
Healthy Diet
- Balanced Nutrition & Juice therapies:
- Eat more fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and lean proteins. A balanced diet provides essential nutrients without excess calories.
- Reduce Unhealthy Foods: Cut down on foods high in sugar, salt, and unhealthy fats. Avoid sugary drinks and high-calorie snacks.
- Portion Control: Be mindful of portion sizes to avoid overeating. Using smaller plates and measuring portions can help.
Regular Exercise
- Stay Active: Aim for at least 150 minutes of moderate exercise each week. This can include activities like brisk walking, swimming, or cycling.
- Strength Training: Include strength training exercises at least two days a week. Building muscle helps increase metabolism and burn calories.
- In order to lose weight, it is essential to burn more calories than those ingested.
Behavior Changes
- Stress Management: Practice stress-reducing techniques like meditation, yoga, or deep breathing exercises. Managing stress can prevent emotional eating.
- Get Enough Sleep: Aim for 7-9 hours of sleep each night. Lack of sleep can affect hormones that regulate hunger and appetite.
- Seek Support: Reach out to friends, family, or a support group for encouragement. Having a support system can make lifestyle changes easier to maintain.
Medical Help
- Consult a Doctor: Work with a healthcare provider to create a personalized weight loss plan. They can offer guidance and monitor your progress.
- Medication: In some cases, medications may be prescribed to help with weight loss. These are typically used alongside lifestyle changes.
- Surgery: For severe obesity, weight-loss surgery (bariatric surgery) may be an option. This is usually considered when other methods have not been successful.

LOSING WEIGHT THROUGH DRINKING!
We must that emphasize that the positive aspect of a weight-loss cure based on juices does not only consist on the fruits & veges consumed , but also in the products that are no-longer consumed: meat, cheese, fried foods, trans fats e.t.c
- CUCUMBER-APPLE-CELERY JUICE– Take out fresh green apples, celery, Cucumbers, Ginger, Lemon, add a little water and churn it in a blender. Filter the juice and drink it. Cucumber is diuretic and purifying & contains tartronic acid which prevents conversion of sugars into fats.
- Pineapple-Hibiscus JUICE – Pineapple, Hibiscus powder, Lemon, Ginger/Garlic, Sweetened with honey, jaggery or stevia.
- Papaya – BEET- LEMON JUICE – In a glass of boiling water, add beets, lemon slices plus other ingredients: Ginger. Add Papaya juice and have this decoction when warm. Papaya is an essential ingredient to reduce abdominal circumference.
- OTHER JUICES
- CHIA WATER DRINK – Chia seeds and lemon juice
- GRAPEFRUIT JUICE – Grapefruit
- Green smothies – Prunes, figs, kiwi,orange/carrot juice, mint leaves
FAT BURNING SPICES – Cayenne pepper, cinnamon, turmeric.



N/B Contraindications of the weight-loss cure – It is not beneficial for some individuals under specific circumstances to carry out a juice-based weight-loss program – Pregnant women, children, nursing mothers, Anemia, hepatic/renal disease, Pre-Post operative stage, convalescents of debilitating illnesses
CONCLUSION
Obesity is a serious health condition that requires a comprehensive approach to manage effectively. By understanding the basics of obesity and making healthy lifestyle changes, you can improve your overall health and reduce the risk of associated health problems. If you are struggling with obesity, seek support from healthcare professionals who can provide personalized guidance and support. Remember, small, sustainable changes can lead to significant improvements in your health and well-being.